Demystifying Electric Heating: Convection, Conduction, and Radiation
Have you ever looked into electric heating and found yourself puzzled by unfamiliar jargon? Terms like convection, conduction, and radiation may have caught your eye, but what exactly do they mean. Fear not – we’re here to simplify it all.
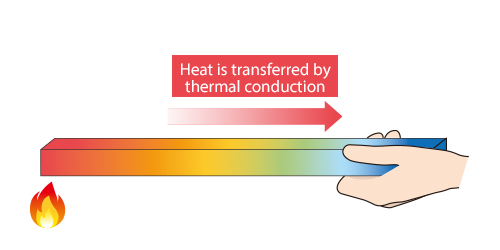
Conduction
Conduction denotes the process by which heat is transferred through solid materials. In solids, particles are tightly bound, so when one particle is warmer than its surroundings due to a direct heat source, it vibrates with energy. Consequently, it collides with adjacent particles, causing them to warm up as well. Gradually, this warmth diffuses throughout the entirety of the solid, raising its temperature.
Think of it as a domino effect of cosy temperatures. As each particle passes along its energy, the warmth spreads raising the overall temperature of the object.
This is the type of warmth you feel when touching a warm object, like the car steering wheel when the car has been left in the sun or taking the fresh toast out of the toaster.
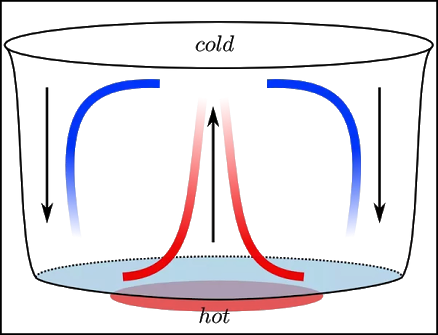
Convection
Convection harnesses the power of air to transmit heat. As cold air flows over a heat source, it undergoes a transformation, warming up and generating convection currents. This perpetual cycle continues as long as the heat source remains stable, resulting in a continuous circulation of warm air.
Unlike solids, particles in the air are unconfined and possess the freedom to move around. Due to their increased spatial freedom, hot air is lighter and less dense than its cooler counterpart, causing it to rise. Think of a hot air balloon rising up! However, this can lead to an uneven distribution of warmth, resulting in the lower half of a room being relatively colder than the upper half.
You can see convection in the steam coming off a hot bath or a saucepan, or you can feel it on a windy day when you feel cooler regardless of the actual temperature.
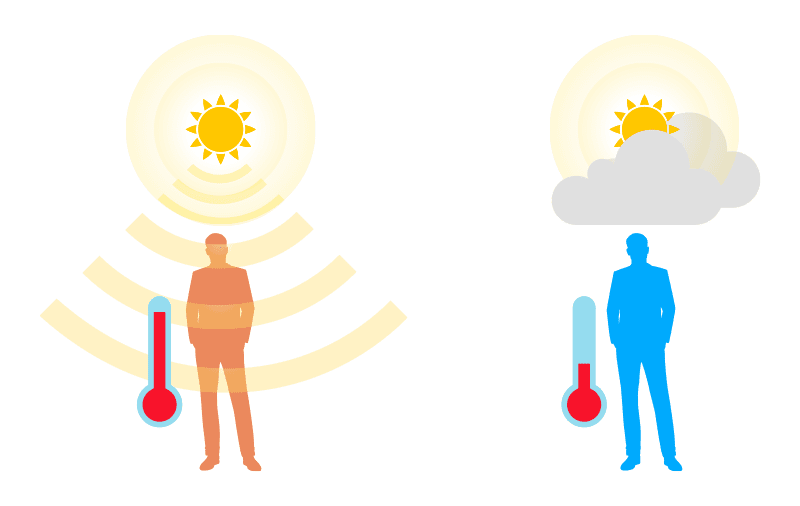
Radiation
Don’t worry, it’s not as daunting as it sounds.
We are constantly surrounded by safe forms of radiation, from our car radios to kitchen microwaves. Even the light illuminating this sentence is a type of radiation. When it comes to maintaining warm homes, radiant warmth proves to be one of the most versatile and effective methods.
Radiant warmth travels invisibly in the form of waves, delivering direct and encompassing heat. When these waves encounter an object, such as an armchair, heat is absorbed and seamlessly transferred.
The absorbed heat is subsequently emitted back into the surroundings, creating a comforting bubble of warmth that can be enjoyed for prolonged periods. Consequently, radiant heating serves as an exceptional primary heating source, as well as a suitable solution for intermittent requirements.
This is the type of warmth you feel when standing close to a fire or when it feels cooler when the sun goes behind a cloud.
In Summary
- Conduction refers to heat transfer through solid materials.
- Convection utilises air to circulate and rapidly distribute heat, making it ideal for spaces requiring quick supplementary heating.
- Radiant warmth travels via imperceptible waves, offering direct and comforting heat. This method stores heat within objects, undisturbed by air movement.
Get The Best Of Both Worlds
Sunflow radiators use a balanced mix of 50% convected and 50% radiant warmth ensuring you get the best of both worlds with a warm and cosy home. Although the surface of a heater may become warm to the touch, conduction doesn’t really account for much of the heating in our homes.
With a deeper understanding of these electric heating principles, we trust you are better equipped to make informed decisions regarding your heating needs.
For more information book a FREE home consultation with one of our Heating Experts who will talk you through everything.